Understanding Cognos Audit Reports and Tables
The IBM Cognos platform provides complete auditing capabilities that enable auditing and managing system usage. By default, system messages, errors, and other product details are logged to flat files that reside in the log directory. IBM Cognos BI provides an additional option to output audit usage information to a relational database. With the usage audit data stored in a relational data source, reporting becomes possible. IBM provides a sample audit model that includes several sample reports to assist in providing immediate benefit from the audit data. In this article, we’re going to discuss specific audit tables and activities to tailor your auditing needs.
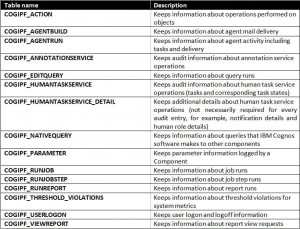
After an audit database has been added to the configuration parameters in IBM Cognos Configuration, the audit database schema is added to the database (at next restart). The audit database is composed of 18 tables, but really only 11 are used for auditing usage.
Many organizations only utilize the provided Audit model and sample reports, but there is much more to be gained if you understand where audit information is stored and how it is logged. Understanding these audit tables allows you to create your customized audit reports.
Audit Tables
Listed below is a matrix of tables and their use:
Audit tables typically not used:
– The COGIPF_SYSPROPS table contains a single record that indicates logging version detail.
– The COGIPF_MIGRATION table is reserved for an upcoming migration application.
– The COGIPF_THRESHOLD_VIOLATIONS records metric threshold exception details that are derived from the IBM Cognos BI system metrics.
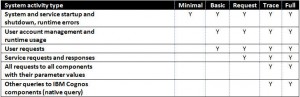
The level of detail can be specified within IBM Cognos Connection to tailor just how much audit information you want back. Below is a matrix of the five possible auditing levels as well as their associated activity types.
Auditing Logon
Logon related information can be recorded by enabling auditing for the IBM Cognos Content Manager service. Audit data related to login to IBM Cognos Connection are stored in following tables:
– COGIPF_USERLOGON
– COGIPF_ACTION
The primary information related to the user logon (e.g. user name and authenticating namespace) is contained in the COGIPF_USERLOGON table, and secondary information such as group membership is recorded in the COGIPF_ACTION table. The namespace that the user belonged to is recorded, so it becomes possible to identify users from different business units if they are not part of the same security namespace.
The same login operation records two audit entries in the COGIPF_ACTION table. The only record that is important from an audit standpoint is the record that queries the security namespace for the group membership of the user. When users log out of the application, a single record is written to both the COGIPF_USERLOGON and COGIPF_ACTION tables.
Records are logged to the audit database, which shows logon operations and sessions expiring due to inactivity. The default inactivity timeout is 60 minutes. In a busy environment where many users are logging in, the records are not consecutive and therefor are hard to correlate. To identify corresponding entries, the records must be matched on COGIPF_SESSIONID table.
Tracking user authentication is crucial for identifying usage patterns and license management. The ability to track unsuccessful login attempts is critical for identifying unauthorized user access. Whenever an unsuccessful login attempt occurs, a record is written to the COGIPF_USERLOGON table.
Examining the COGIPF_ERRORDETAILS column reveals the true source of the failure. Because the audit record only indicates a success or failure status, paying attention to the error details is important when trying to isolate unauthorized access to the application versus users incorrectly typing their passwords. In the case of incorrect passwords, the records are identical except for the error details.
The audit package provided as part of the IBM Cognos BI Samples contains various reports that are intended as a head start to begin the analysis of audit data. Additional information regarding the configuration and deployment of the audit reports can be found as part of the core product documentation.
The standard auditing features that come out of the box with IBM Cognos 10 BI cover many aspect of audit operation. However some areas such as the auditing the users and capability assignments are not included. IBM provides Cognos 10 Audit Extension application that extensively covers Account Audit, Content Audit, Status Audit and Role / Capability Audit. This application is designed for IBM Cognos BI 10 and also intended to interact with any third party application that can issue commands via web services.