Data Governance: A Practical Guide to Sustainable Data Practices
Credit unions have long been pioneers in member-centric banking, building lasting relationships through personalized services and community-based values. Today’s credit unions operate in an increasingly complex regulatory environment with heightened expectations around data privacy and security. Balancing these growing compliance demands within operational constraints while maintaining personalized service presents unique challenges—demonstrating data stewardship to regulators, protecting member privacy, and maintaining member trust through responsible data management.
Data governance is a comprehensive solution to these interconnected challenges, providing the framework to address regulatory requirements, meet evolving member privacy expectations, and strengthen the foundation of member trust that is fundamental to credit union success.
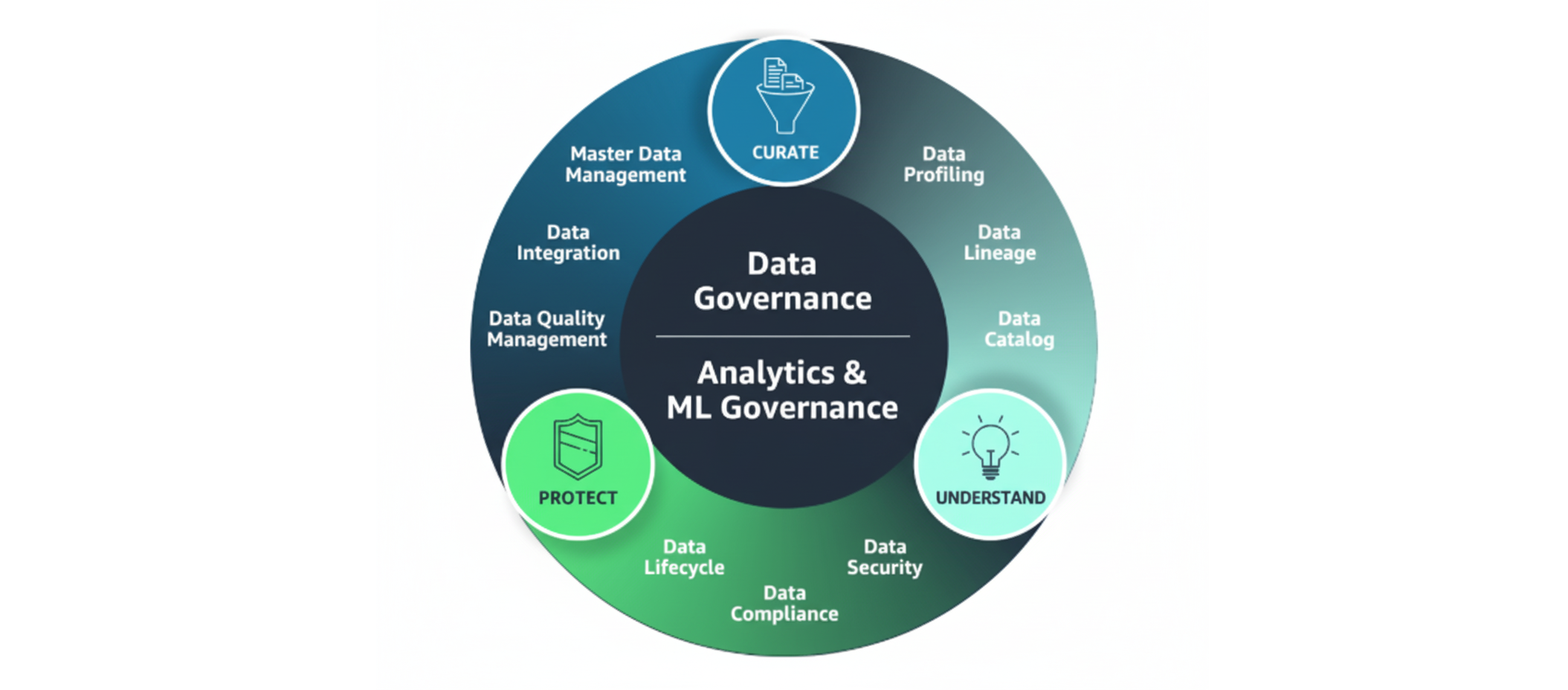
What Data Governance Delivers
Data governance is the systematic management of data availability, usability, integrity, and security throughout your organization. For credit unions, this means establishing clear policies for how member data is collected, stored, used, and protected—creating the foundation that enables confident decision-making, regulatory compliance, and personalized service.
“Credit Unions leverage the strength of customer intimacy with their members. As business becomes more digital and data-driven, the need to govern that data well becomes even more critical for credit unions, to avoid the risk bad data can impart on this core strategy. Solid data governance mitigates this risk.”
— Paul Hardy, EVP Professional Services & Head of Data Strategy
Immediate Value
Regulatory Compliance: Quickly locate required information and prove compliance during examinations through clear documentation and access controls. And, be sure to implement regulatory best practices such as:
- Documentation: Maintain documentation demonstrating program effectiveness
- Privacy and Security: Stay current with evolving regulations and maintain appropriate safeguards
- Third-Party Risk: Ensure your governance framework addresses vendor data handling
Member Privacy and Trust: Prevent privacy breaches through appropriate access controls and transparency about information use
Data Quality: Eliminate duplicate records and inefficient processes through standards for data entry and validation
Strategic Decisions: Trust information used for planning through clear definitions and consistent calculations
How To Get Started
- Establish Data Ownership: Assign individuals responsibility for data domains—member information, loans, financial reporting. These stewards must understand business requirements and work with IT teams to ensure proper system implementation.
- Document Current State: Inventory what data you collect, where it’s stored, and how it’s used. Identify gaps in quality, access controls, and retention policies to prioritize improvements.
- Implement Policy Framework: Develop written policies for data collection, use, sharing, and retention that align with regulations and support operations. Include quality standards, access controls, retention schedules, and escalation procedures.
- Collaborate: Third party experts can provide perspectives on best practices from both inside and outside the industry.
Measuring Success
Track both operational metrics (data quality scores, issue resolution times, examination findings) and strategic outcomes (compliance scores, member satisfaction, operational efficiency).

Bottom Line
Effective data governance is an ongoing commitment to responsible data stewardship. Start with fundamental practices within current resources, then build capabilities as your program matures. Credit unions investing in data governance today will be better positioned to serve members, satisfy regulators, and compete effectively. Your members’ trust and long-term success depend on it.



